Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Case Reports
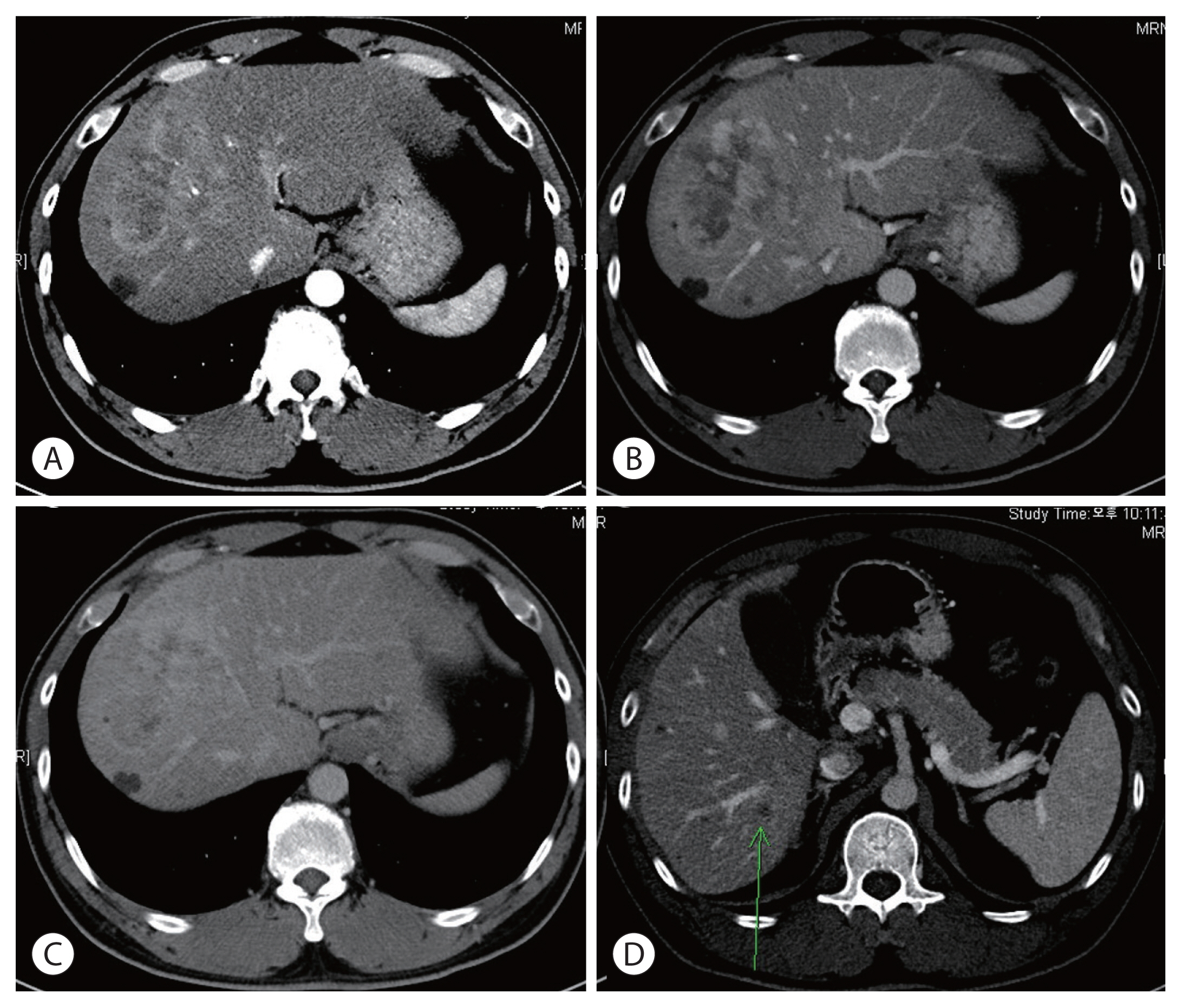
- Long-term survival after CCRT and HAIC followed by ALPPS for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein invasion: a case report
- In-Jung Kim, Sung Hwan Yoo, Jung Il Lee, Kwan Sik Lee, Hyun Woong Lee, Jin Hong Lim
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(1):84-90. Published online March 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.03.07
- 2,790 Views
- 70 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - There are various methods for treating advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein invasion, such as systemic chemotherapy, transarterial chemoembolization, transarterial radioembolization, and concurrent chemoradiotherapy. These methods have similar clinical efficacy but are designed with a palliative aim. Herein, we report a case that experienced complete remission through “associating liver partition and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy (ALPPS)” after concurrent chemoradiotherapy and hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy. In this patient, concurrent chemoradiotherapy and hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy induced substantial tumor shrinkage, and hypertrophy of the nontumor liver was sufficiently induced by portal vein ligation (stage 1 surgery) followed by curative resection (stage 2 surgery). Using this approach, long-term survival with no evidence of recurrence was achieved at 16 months. Therefore, the optimal use of ALPPS requires sufficient consideration in cases of significant hepatocellular carcinoma shrinkage for curative purposes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Is multidisciplinary treatment effective for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus?
Won Hyeok Choe
Journal of Liver Cancer.2022; 22(1): 1. CrossRef
- Is multidisciplinary treatment effective for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus?

- A Case of a Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Lung Metastasis Who Failed Sorafenib Treatment and Achieved Complete Remission after Lung Resection and Radiation Therapy
- Jung Hwan Yu, Jung Il Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2017;17(1):77-81. Published online March 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.17.1.77
- 1,478 Views
- 17 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), sorafenib is the only approved systemic chemotherapy, and has been applied for those with advanced HCC especially with systemic metastasis. However, the treatment results are suboptimal leaving many cases with disease progression despite the use of optimum dose. There is no established guideline for those that fail to respond to sorafenib treatment. In this case, a 46-years-old male with metastatic lung cancer from HCC experienced progression despite sorafenib treatment. Then, the patient received surgical resection of the metastatic lung mass followed by radiation therapy and achieved complete remission for 10 months after the surgical treatment and radiation therapy. Alpha-fetoprotein level was normalized and complete remission has been maintained.

- Bronchobiliary Fistula after Transarterial Chemoembolization and Radiotherapyfor Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Bile Duct Invasion
- Jungran Choi, Yoomi Park, Kwangwon Rhee, Daewon Ma, Ja Kyung Kim, Jung Il Lee, Kwan Sik Lee, Kwang-Hun Lee, Seokjin Haam
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2013;13(2):173-177. Published online September 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.13.2.173
- 898 Views
- 2 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Trans-arterial chemoembolization (TACE) is widely used in the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Its common complications are right upper quadrant pain, nausea, vomiting, whereas some rare complications include focal pancreatic necrosis, gastric ulcer, renal failure, DIC, biliary tree necrosis and splenic infarction. Bronchobiliary fistula (BBF) is a rare complication that consists of the formation of a passageway between the biliary system and the bronchial tree. We report a case of BBF due to previous TACE for HCC.

- A Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma Invading the Intrahepatic Duct Confirmed by Percutaneous Transhepatic Cholangioscopy
- Byoung Wook Bang, Seok Jeong, Yong Sun Jeon, In Suh Park, Don Haeng Lee, Jung Il Lee, Kye Sook Kwon, Hyung Gil Kim, Yong Woon Shin, Young Soo Kim, Jin-Woo Lee
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2008;8(1):74-76. Published online June 30, 2008
- 523 Views
- 6 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) invading the bile duct is an uncommon form and sometimes difficult to differentiate from cholangiocarcinoma. Because of different treatment modality, differential diagnosis of thesetwo diseases should be performed. We experienced an unusual case with HCC with obstructive jaundice caused by the involvement of intrahepatic duct, then confirmed by percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopic biopsy results. A 60-year-old man was admitted with fever, chills, and an epigastric pain of 5 days duration. The patient had compensated liver cirrhosis as a result of alcohol abuse. Multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) of the abdomen revealed a low attenuated mass associated with bile duct dilation at the fourth segment of the liver. The cholangioscopic finding showed a single, 2-cm, polypoid mass with a yellowish ‘‘chicken fat-like’’ appearance, protruding into the lumen of the fourth branch of the left intrahepatic duct and bleeding easily. A diagnosis of HCC was proven by microscopic examination of the tissue specimen obtained by a cholangioscopic biopsy.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter